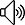AccountManager.addAccount()
?
public AccountManagerFuture<Bundle> addAccount(final String accountType,
final String authTokenType, final String[] requiredFeatures,
final Bundle addAccountOptions,
final Activity activity, AccountManagerCallback<Bundle> callback, Handler handler) {
...
}
?
?
在程序中創(chuàng)建指定類(lèi)型的系統(tǒng)帳號(hào),需要提供一個(gè)AccountManagerCallback類(lèi)型的回調(diào),后面會(huì)講到其作用。
本方法要求用戶(hù)添加指定類(lèi)型的帳號(hào)。
此種帳號(hào)類(lèi)型對(duì)應(yīng)的authenticator將加載對(duì)應(yīng)的UI來(lái)處理這個(gè)請(qǐng)求。
方法返回一個(gè)AccountManagerFuture對(duì)象,可解析出一個(gè)Bundle,包含以下信息:
- KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME: 創(chuàng)建的帳號(hào)的名稱(chēng)
- KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE: 帳號(hào)類(lèi)型
本方法創(chuàng)建一個(gè)匿名AmsTask實(shí)例并啟動(dòng):
?
return new AmsTask(activity, handler, callback) {
public void doWork() throws RemoteException {
mService.addAcount(mResponse, accountType, authTokenType,
requiredFeatures, activity != null, optionsIn);
}
}.start();
這里,以異步的方式請(qǐng)求AccountManagerService.addAccount()
start()方法立即返回,返回值是AccountManagerFuture類(lèi)型的。
?
AccountManagerService.addAccount()
這個(gè)方法中,創(chuàng)建一個(gè)Session類(lèi)型的匿名實(shí)例,并調(diào)用其bind()方法,最終捆綁到應(yīng)用程序提供的authenticator service:
?
new Session(accounts, response, accountType, expectActivityLaunch,
true /* stripAuthTokenFromResult */) {
public void run() throws RemoteException {
mAuthenticator.addAccount(this, mAccountType, authTokenType, requiredFeatures,
options);
}
protected String toDebugString(long now) {
return super.toDebugString(now) + ", addAccount"
+ ", accountType " + accountType
+ ", requiredFeatures "
+ (requiredFeatures != null
? TextUtils.join(",", requiredFeatures)
: null);
}
}.bind();
這是Session.bind()方法的相關(guān)細(xì)節(jié):
?
?
void bind() {
...
if (!bindToAuthenticator(mAccountType)) {
Log.d(TAG, "bind attempt failed for " + toDebugString());
onError(AccountManager.ERROR_CODE_REMOTE_EXCEPTION, "bind failure");
}
}
bindToAuthenticator()方法找到對(duì)應(yīng)的組件名稱(chēng)(應(yīng)用程序中定義的相關(guān)service),并且對(duì)Service發(fā)起綁定:
?
?
private boolean bindToAuthenticator(String authenticatorType) {
final AccountAuthenticatorCache.ServiceInfo<AuthenticatorDescription> authenticatorInfo;
authenticatorInfo = mAuthenticatorCache.getServiceInfo(
AuthenticatorDescription.newKey(authenticatorType), mAccounts.userId);
...
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(AccountManager.ACTION_AUTHENTICATOR_INTENT);
intent.setComponent(authenticatorInfo.componentName);
...
if (!mContext.bindService(intent, this, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE, mAccounts.userId)) {
...
}
return true;
}
Session類(lèi)實(shí)現(xiàn)了ServiceConnection接口,因此,當(dāng)成功綁定到對(duì)應(yīng)的應(yīng)用程序中的Service,其實(shí)現(xiàn)的onServiceConnected()方法將被調(diào)用:
?
?
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mAuthenticator = IAccountAuthenticator.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
run();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
onError(AccountManager.ERROR_CODE_REMOTE_EXCEPTION,
"remote exception");
}
}
這里的service,即是AbstractAuthenticator抽象類(lèi)提供的IBinder:
?
?
public abstract class AbstractAccountAuthenticator {
...
private class Transport extends IAccountAuthenticator.Stub {
public void addAccount(IAccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType,
String authTokenType, String[] features, Bundle options)
throws RemoteException {
...
try {
final Bundle result = AbstractAccountAuthenticator.this.addAccount(
new AccountAuthenticatorResponse(response),
accountType, authTokenType, features, options);
...
}
...
}
...
}
...
private Transport mTransport = new Transport();
/**
* @return the IBinder for the AccountAuthenticator
*/
public final IBinder getIBinder() {
return mTransport.asBinder();
}
...
}
AbstractAccountAuthenticator的內(nèi)部類(lèi)Transport是IAccountAuthenticator接口的一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn)。后者規(guī)定了Authenticator的一組行為。
以添加帳號(hào)的操作為例,作為接口實(shí)現(xiàn)的Transport的addAccount()方法調(diào)用了AbstractAccountAuthenticator類(lèi)的addAccount()抽象方法,這個(gè)方法的具體實(shí)現(xiàn),則由應(yīng)用程序中定義的authenticator子類(lèi)來(lái)完成。
這里涉及到IPC,應(yīng)用程序是服務(wù)端,提供服務(wù)的實(shí)現(xiàn),而AccountManagerService則是客戶(hù)端,負(fù)責(zé)通過(guò)代理對(duì)象發(fā)起調(diào)用。
?
Email的authenticator實(shí)現(xiàn):
?
class PopImapAuthenticator extends AbstractAccountAuthenticator {
...
@Override
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType,
String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options)
throws NetworkErrorException {
// There are two cases here:
// 1) We are called with a username/password; this comes from the traditional email
// app UI; we simply create the account and return the proper bundle
if (options != null && options.containsKey(OPTIONS_PASSWORD)
&& options.containsKey(OPTIONS_USERNAME)) {
final Account account = new Account(options.getString(OPTIONS_USERNAME),
AccountManagerTypes.TYPE_POP_IMAP);
AccountManager.get(PopImapAuthenticatorService.this).addAccountExplicitly(
account, options.getString(OPTIONS_PASSWORD), null);
...
Bundle b = new Bundle();
b.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME, options.getString(OPTIONS_USERNAME));
b.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE, AccountManagerTypes.TYPE_POP_IMAP);
return b;
// 2) The other case is that we're creating a new account from an Account manager
// activity. In this case, we add an intent that will be used to gather the
// account information...
} else {
Bundle b = new Bundle();
Intent intent =
AccountSetupBasics.actionSetupPopImapIntent(PopImapAuthenticatorService.this);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE, response);
b.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent);
return b;
}
}
1) 如果是Email應(yīng)用程序內(nèi)部添加新的電子郵件帳號(hào),此時(shí)已經(jīng)取得了帳號(hào)的用戶(hù)名和密碼,那么直接創(chuàng)建對(duì)應(yīng)的系統(tǒng)帳號(hào),并調(diào)用AccountManager.addAccountExplicitly()將其添加到系統(tǒng)帳號(hào)數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)中,并返回帳號(hào)名稱(chēng)和類(lèi)型。
2) 如果是從外部,比如系統(tǒng)設(shè)置中添加Email帳號(hào),則創(chuàng)建指向Email應(yīng)用中創(chuàng)建帳號(hào)對(duì)應(yīng)的activity的Intent,并返回。這樣,AmsTask實(shí)例在完成時(shí)會(huì)通過(guò)Handler機(jī)制調(diào)用AddAccountSettings活動(dòng)提交的一個(gè)回調(diào):
?
?
private AccountManagerCallback<Bundle> mCallback = new AccountManagerCallback<Bundle>() {
public void run(AccountManagerFuture<Bundle> future) {
boolean done = true;
try {
Bundle bundle = future.getResult();
//bundle.keySet();
Intent intent = (Intent) bundle.get(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT);
if (intent != null) {
done = false;
Bundle addAccountOptions = new Bundle();
addAccountOptions.putParcelable(KEY_CALLER_IDENTITY, mPendingIntent);
addAccountOptions.putBoolean(EXTRA_HAS_MULTIPLE_USERS,
Utils.hasMultipleUsers(AddAccountSettings.this));
intent.putExtras(addAccountOptions);
startActivityForResult(intent, ADD_ACCOUNT_REQUEST);
...
}
這樣就會(huì)啟動(dòng)Email創(chuàng)建帳號(hào)的activity,之后又會(huì)走到1)中的步驟了。
?
?
基于Andoird 4.2.2的Account Manager源代碼分析學(xué)習(xí):創(chuàng)建選定類(lèi)型的系統(tǒng)帳號(hào)
更多文章、技術(shù)交流、商務(wù)合作、聯(lián)系博主
微信掃碼或搜索:z360901061

微信掃一掃加我為好友
QQ號(hào)聯(lián)系: 360901061
您的支持是博主寫(xiě)作最大的動(dòng)力,如果您喜歡我的文章,感覺(jué)我的文章對(duì)您有幫助,請(qǐng)用微信掃描下面二維碼支持博主2元、5元、10元、20元等您想捐的金額吧,狠狠點(diǎn)擊下面給點(diǎn)支持吧,站長(zhǎng)非常感激您!手機(jī)微信長(zhǎng)按不能支付解決辦法:請(qǐng)將微信支付二維碼保存到相冊(cè),切換到微信,然后點(diǎn)擊微信右上角掃一掃功能,選擇支付二維碼完成支付。
【本文對(duì)您有幫助就好】元